

Medshotsalmost 9 years ago
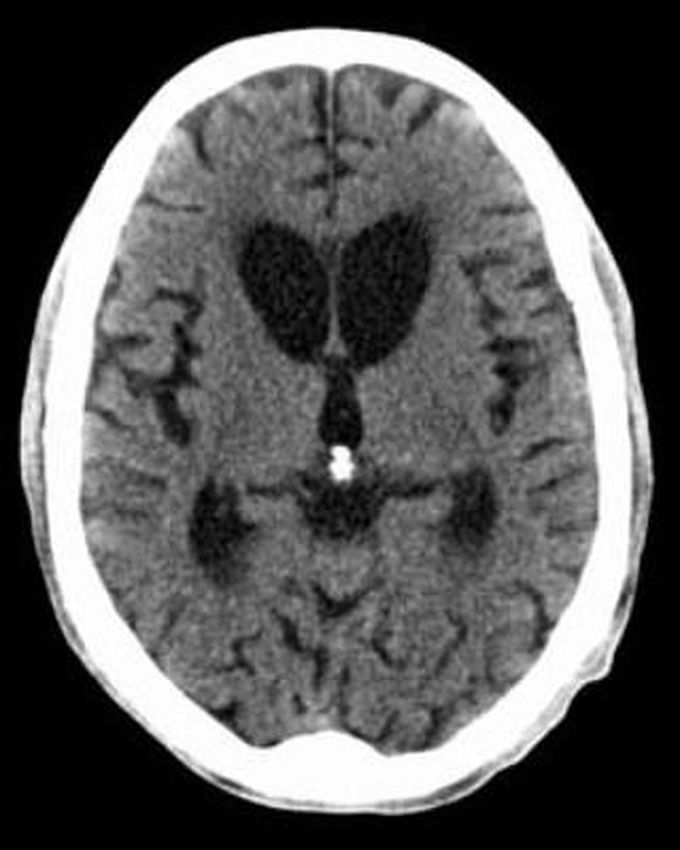
Case of Huntington's Disease
Huntington's disease is an autosomal dominant disease that is known by mutation on chromosome 4 with CAG trinucleotide repeates itself. Presentation is a young patient with a movement disorder, dementia, depression, aggression/psychosis. Key neurologic findings are atrophy of caudate nucleus seen on CT/MRI, decrease in GABA and Ach, increase in dopamine. Management is by using rivastigmine and tetrabenzine as they inhibit VMAT and increase neurotransmitter degradation by MAO. while haloperidol is used for psychotic symptoms and aggression. Note the atrophy of caudate nucleus on the MRI Image.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Dandy Walker Malformation | Diagnosis symptoms and treatment2-Minute Neuroscience: Brain AneurysmsSeizures (Epilepsy) Nursing NCLEX: Tonic-Clonic, Generalized, Focal, SymptomsStroke: Causes, Risk Factors, Treatment, and Prevention | Mass General BrighamPreparation for USMLEScope of practice of NREMTSuturingNeurofibromatosisAbsence seizuresSymptoms of absence seizures

