
Medicogramabout 8 years ago
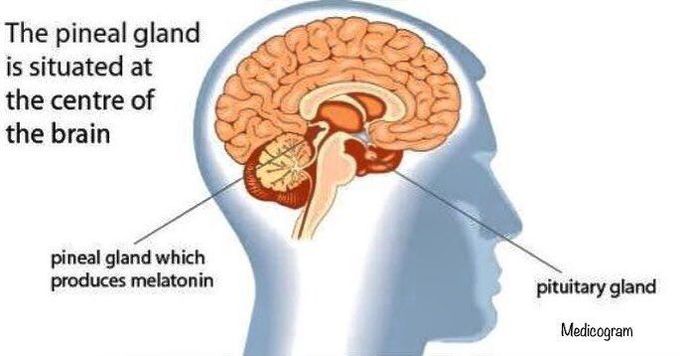
What is Melatonin?Melatonin is a natural hormone made by your body's pineal (pih-knee-uhl) gland. This is a pea-sized gland located just above the middle of the brain. During the day the pineal is inactive. When the sun goes down and darkness occurs, the pineal is "turned on" by the SCN and begins to actively produce melatonin, which is released into the blood. Usually, this occurs around 9 pm. As a result, melatonin levels in the blood rise sharply and you begin to feel less alert. Sleep becomes more inviting. Melatonin levels in the blood stay elevated for about 12 hours - all through the night - before the light of a new day when they fall back to low daytime levels by about 9 am. Daytime levels of melatonin are barely detectable.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Gross Features of Diencephalon: A TutorialFunctional Anatomy and Clinical Correlation of Thalamus, Epithalamus, and HypothalamusPineal Body: Location, Development and HistologyOverview of Pineal Gland HistologyBrain Sand of Pineal GlandHernia and its typesX-ray of a contortionist performing an exercise!!
🍄 Commonly noticed Triads; Pentads🍚🍚 1. Hutchinson's Triad (congenital syphilis): - Hutchinson's teeth (notched incisors) - Interstitial keratitis - Deafness due to involvement of the eighth cranial nerve 2. Charcot's Triad(for cholangitis): - Jaundice - Fever with chills - Right upper quadrant pain 3. Samter's triad -bronchial asthma -nasal polyps - aspirin intolerance 4. Triad of O'Donoghue (or unhappy triad, often seen in sports injuries, especially knee injuries): - ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) tear - MCL (medial collateral ligament) tear - Medial meniscus tear 5. Beck's Triad (cardiac tamponade): - Distant/muffled heart sounds - Increased jugular venous pressure - Hypotension 6. Saint's Triad: - Gallstones - Diverticulosis - Hiatal hernia 7. Whipple's Triad: - Symptoms of hypoglycemia - Documented low blood sugar - Relief of symptoms after glucose administration 8. Cushing's Triad (seen in increased intracranial pressure): - Hypertension - Bradycardia - Irregular or abnormal respirations 9. Virchow's Triad(risk factors for thrombosis): - Endothelial injury - Stasis or turbulent blood flow - Blood hypercoagulability 10. Triad of Alport Syndrome: - Hematuria - Sensorineural hearing loss - Ocular abnormalities 11. Reynold's Pentad (an extension of Charcot's Triad for advanced cholangitis): - Jaundice - Fever with chills - Right upper quadrant pain - Septic shock - Mental confusion
🍄 Commonly noticed Triads; Pentads🍚🍚 1. Hutchinson's Triad (congenital syphilis): - Hutchinson's teeth (notched incisors) - Interstitial keratitis - Deafness due to involvement of the eighth cranial nerve 2. Charcot's Triad(for cholangitis): - Jaundice - Fever with chills - Right upper quadrant pain 3. Samter's triad -bronchial asthma -nasal polyps - aspirin intolerance 4. Triad of O'Donoghue (or unhappy triad, often seen in sports injuries, especially knee injuries): - ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) tear - MCL (medial collateral ligament) tear - Medial meniscus tear 5. Beck's Triad (cardiac tamponade): - Distant/muffled heart sounds - Increased jugular venous pressure - Hypotension 6. Saint's Triad: - Gallstones - Diverticulosis - Hiatal hernia 7. Whipple's Triad: - Symptoms of hypoglycemia - Documented low blood sugar - Relief of symptoms after glucose administration 8. Cushing's Triad (seen in increased intracranial pressure): - Hypertension - Bradycardia - Irregular or abnormal respirations 9. Virchow's Triad(risk factors for thrombosis): - Endothelial injury - Stasis or turbulent blood flow - Blood hypercoagulability 10. Triad of Alport Syndrome: - Hematuria - Sensorineural hearing loss - Ocular abnormalities 11. Reynold's Pentad (an extension of Charcot's Triad for advanced cholangitis): - Jaundice - Fever with chills - Right upper quadrant pain - Septic shock - Mental confusion

